Everything About Gout (Nickris Wind): What It Is, What Causes It, and How to Treat It at Home
Gout, sometimes referred to in traditional medicine as “Nickris wind,” is a metabolic disorder that primarily affects the joints, but its impact can extend to multiple organs in the body. The disease develops due to a disruption in nucleic acid metabolism, which leads to a significant increase in uric acid levels in the blood and tissues. When uric acid accumulates, it forms crystals that deposit in joints, kidneys, the ear cartilage, and even organs such as the heart, eyes, and brain membranes. Although gout can affect several organs, joint involvement is typically the earliest and most noticeable symptom.
Who Is at Risk?
Gout occurs more frequently in men over the age of 40, while women are affected less often, usually after menopause. The disease can also have a hereditary component, meaning that people with family members who have gout are more likely to develop it themselves. Gout tends to be a chronic condition, characterized by long periods of persistent symptoms that are occasionally interrupted by sudden, acute attacks.
Acute Gout Attacks
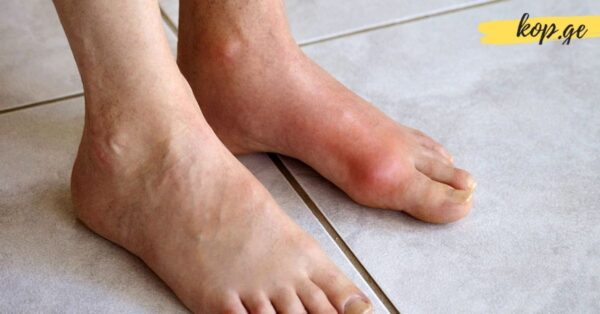
An acute gout attack often begins at night or early in the morning. These attacks are usually preceded by a general feeling of malaise and increased urination. Certain dietary and lifestyle factors can trigger these attacks, including consuming large amounts of meat, fish, or eggs—especially fried foods—as well as alcohol consumption. Viral infections, minor injuries, or trauma can also provoke a flare-up. Acute attacks can last anywhere from three hours to 24 hours and are usually extremely painful, often affecting a single joint, such as the big toe, ankle, or knee.
Chronic Gout
Chronic gout develops over time when uric acid crystals continue to accumulate in the joints. This leads to persistent changes in the affected joint, including swelling, redness, limited mobility, and changes in shape or thickness of the joint itself. Chronic gout can result in deformities if left untreated.
Lifestyle Recommendations
If you are dealing with gout, certain lifestyle habits can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of attacks:
Diet: Focus on reducing purine-rich foods like red meat, organ meats, certain seafood, and fried eggs. Incorporate more vegetables, fruits, and whole grains into your diet.
Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help flush uric acid from the body.
Physical Activity: Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight and improves circulation, reducing the risk of crystal deposits in joints.
Warmth: Keeping the affected joint warm can help reduce pain and stiffness.
Home Remedies for Gout
1. Nettle (Urtica dioica) Infusion
Fresh nettle shoots can help reduce uric acid levels and alleviate inflammation in the joints. Chop 1 tablespoon of fresh nettle leaves and pour 1 cup of boiling water over them. Let it steep for one hour, then strain. Drink 2 tablespoons of this infusion two to three times a day before meals. Alternatively, extract fresh nettle juice and consume 1 teaspoon two to three times daily.
2. Walnut Leaf or Green Walnut Infusion
Pour 1 cup of boiling water over 20 grams of young walnut leaves or unripe walnuts. Let the mixture steep for one hour, then strain. Take 1 tablespoon of the infusion three times a day. This remedy helps reduce inflammation and supports kidney function, aiding the removal of uric acid from the body.
3. White-Headed Cabbage
During a flare-up, consuming white-headed cabbage in any form—especially raw in salads—can help neutralize uric acid and reduce joint pain.
4. Black Hawthorn Berries
Black hawthorn berries, whether in tea, infused with honey, or sweetened slightly, can be beneficial for gout. They help maintain healthy blood circulation and support kidney function, assisting in uric acid elimination.
Topical Remedies for Joint Pain
1. Horse Chestnut (Aesculus hippocastanum) Decoction
Grind 1 tablespoon of horse chestnut and pour 200 ml of boiling water over it. Let it steep for one hour. This decoction can be used as a warm compress on painful joints to reduce swelling and inflammation.
2. Ant Alcohol Tincture
Mix 5 drops of ant alcohol tincture with 1 tablespoon of water and apply to inflamed joints. This remedy has anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties.
3. Mallow Leaves in Milk
Apply mallow leaves boiled in milk to the affected joints. This natural compress helps soothe pain and reduce inflammation.
Gout Bath
Prepare a bath to relieve joint pain and inflammation: take 100 grams of chamomile flowers and pour them into 10 liters of water. Bring to a gentle boil for 5 minutes, then add 200 grams of table salt. Immerse the painful limb in the bath for 30 minutes, occasionally adding hot chamomile infusion to maintain the temperature. This soothing bath helps improve blood circulation and reduces swelling.
Important Notes
Gout attacks should be carefully monitored, especially in cases of chronic kidney or heart disease.
Avoid self-medicating with over-the-counter anti-inflammatories without consulting a doctor, as these can interact with other conditions.
Always maintain a healthy weight, hydrate adequately, and avoid purine-rich foods to prevent attacks.
Conclusion
While gout is a chronic and potentially painful condition, proper lifestyle management, dietary adjustments, and the use of herbal remedies can help reduce its impact. Regular movement, hydration, and careful attention to nutrition are key to minimizing flare-ups. Herbal infusions, topical compresses, and soothing baths made from plants like nettle, walnut, horse chestnut, and chamomile can complement medical treatment and improve quality of life. By combining these natural remedies with medical supervision, patients can control their symptoms and reduce the frequency of gout attacks.