Beware of pneumonia! How can we recognize it early, and how can we support a faster recovery?
Pneumonia is a serious respiratory condition that often develops as a complication after a viral or bacterial infection. Because a correct diagnosis cannot be made at home, healthcare professionals consistently emphasize the importance of recognizing the early warning signs so that medical help can be sought as soon as possible.
Even with modern medications, advanced diagnostic tools, and improved treatment methods, pneumonia can still be dangerous and, in some cases, life-threatening. Individuals with weakened immune systems, young children, older adults, and people with chronic health conditions—such as cardiovascular disorders or hypertension—may face a higher risk of complications. Detecting the inflammation early is essential, as timely medical attention can help prevent the illness from progressing and may contribute to a smoother recovery.
Early Symptoms of Pneumonia
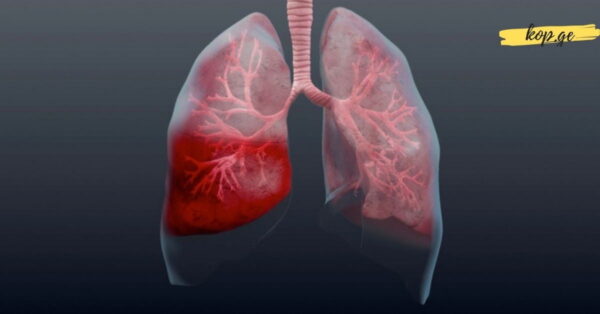
Pneumonia occurs when infectious agents reach the alveoli—tiny air sacs located at the ends of the bronchial passages. These sacs play a vital role in respiration by supplying the bloodstream with oxygen and removing carbon dioxide. When pneumonia develops, the alveoli become filled with inflammatory fluid rather than air, interrupting normal gas exchange and making breathing increasingly difficult.
Fortunately, pneumonia often shows recognizable early signs. Some of the most common include:
High fever that does not respond well to medication.
Persistent temperature elevation may signal an underlying inflammatory process that requires medical evaluation.
Shallow breathing or a sensation of shortness of breath.
People may feel they cannot take a full deep breath, which creates discomfort and anxiety.
Rapid heartbeat and lowered blood pressure.
These signs often indicate that the body is under stress and trying to compensate for reduced oxygen intake.
Chest pain.
Pain may worsen during deep breaths or coughing.
In addition, individuals with pneumonia frequently experience severe weakness, pronounced fatigue, and unusual sleepiness. A deep, persistent cough may develop, often producing sputum that can have a greenish tint characteristic of certain infections. Such symptoms signal the need for medical attention, as only a specialist can evaluate their cause and determine whether pneumonia is present.
What Causes Pneumonia?
The primary cause of pneumonia is an infection of the lung tissue by viruses or bacteria, often occurring when the immune system is weakened. In many cases, pneumonia appears a few days after the initial illness. For example, a person recovering from influenza or another viral infection may feel well enough to return to work but still notice lingering weakness. In some individuals, especially those with compromised immune function, pneumonia may develop without a high fever. This can create a false sense of security, leading the person to believe the symptoms are related to stress or exhaustion rather than a respiratory infection.
In such situations, the only symptom that raises concern might be a painful, persistent cough. Some people attempt to manage this cough with herbal teas or other home remedies, not realizing that a more serious condition may be developing. Recognizing these warning signs helps reduce delays in seeking medical support.
Besides viral or bacterial infections, pneumonia can occasionally develop from other causes, such as:
Fungal infections, which typically affect individuals with weakened immunity
Chemical injury to the lungs, such as from inhaling irritants
Severe hypothermia, which stresses the body and weakens natural defenses
Because pneumonia can arise from different sources, a professional medical evaluation is essential. Doctors often recommend a chest X-ray, which can clearly show areas of inflammation or fluid accumulation within the lungs. This imaging is one of the most reliable methods for confirming the presence of pneumonia.
Why Early Diagnosis Matters
When diagnosed early, pneumonia typically responds well to appropriate medical care and is less likely to lead to complications. Early identification makes it easier for healthcare providers to determine the cause of the inflammation and select the most effective treatment approach. Delaying evaluation allows the infection to progress, making symptoms more severe and recovery more difficult.
Being aware of the common symptoms—such as persistent fever, difficulty breathing, chest discomfort, and unusual fatigue—can help individuals seek help sooner rather than later. It is also advisable to avoid unverified home treatments or inexperienced self-medication, as these can mask symptoms or delay proper care. Following medical recommendations carefully plays a key role in a safer and more efficient recovery process.
Supporting Recovery and Preventing Complications
While only a healthcare professional can diagnose pneumonia and recommend treatment, individuals can support recovery by paying attention to their overall well-being. Rest, hydration, and following medical advice are often important components of the healing process. Because pneumonia can take time to resolve, patience and consistent follow-up with a doctor help reduce the risk of long-term complications.
Physicians may also provide guidance on how to monitor symptoms at home, explain when to return for reassessment, and advise on how to protect others from potential infection. Understanding the nature of the illness empowers patients to participate actively in their own recovery and to recognize signs that may require further evaluation.
Stay Informed and Pay Attention to Your Health
The key message is simple: pneumonia is a serious condition, but recognizing its symptoms early and seeking professional care can make a meaningful difference. Awareness, timely action, and careful adherence to medical guidance all contribute to safer outcomes.
And lastly, a reminder that everyday habits—such as maintaining a balanced lifestyle, supporting the immune system, and paying attention to unusual respiratory symptoms—can help individuals stay healthier overall.