Blood clots in the legs, abdomen, and brain can be extremely dangerous! Here are the symptoms you need to watch out for.
Blood clotting is a serious condition that can be life-threatening if left untreated. Blood clots form when blood thickens and clumps together, blocking normal blood flow through veins or arteries. This can restrict oxygen and nutrient supply to vital organs, leading to severe complications, including heart attacks, strokes, or even death. Because of these risks, it’s crucial to monitor your body regularly and be aware of the early warning signs of blood clots. Ignoring them can have devastating consequences.
Blood Clots in the Legs
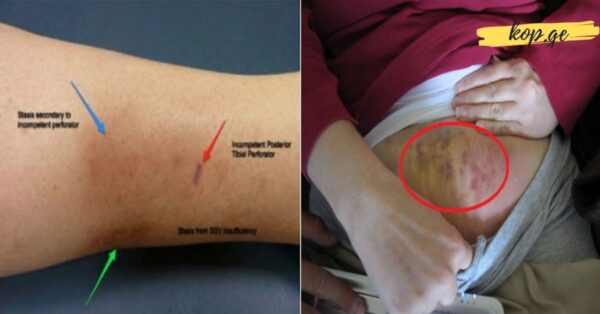
Blood clots in the legs are a common form of deep vein thrombosis (DVT). The danger of DVT is that it often develops without obvious symptoms, making it difficult to detect early. Some warning signs may seem mild or similar to everyday discomfort, which is why vigilance is essential.
Here are key symptoms to watch for:
Swelling in one leg, usually below the knee
Pain or tenderness, often starting in the calf
Discoloration, such as redness or a bluish tint
One method to check for a clot is to gently stretch the toes upward; if pain occurs in the calf or ankle, it may indicate a blood clot. While DVT can occur in other deep veins, it is most commonly found in the legs. If left untreated, a clot can travel to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism, which is life-threatening.
Blood Clots in the Abdomen
Blood clots can also develop in the abdominal veins, leading to a condition that can be difficult to distinguish from other common illnesses, such as food poisoning or a stomach virus. Symptoms of an abdominal blood clot may include:
Severe abdominal pain
Nausea or vomiting
Diarrhea
If you experience these symptoms without another clear cause, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Imaging tests like an ultrasound or CT scan are usually required to confirm the presence of an abdominal clot.
Blood Clots in the Lungs (Pulmonary Embolism)
When a blood clot travels to the lungs, it is called a pulmonary embolism (PE). This condition is extremely dangerous and can be fatal if not treated promptly. Symptoms of a pulmonary embolism include:
Sharp chest pain that may worsen when breathing deeply
Sudden coughing, sometimes with blood
Rapid heartbeat or palpitations
A PE often occurs when a clot from a leg vein breaks free and travels through the bloodstream to the lungs. It requires immediate medical attention and may involve anticoagulant medication to prevent further clotting.
Blood Clots in the Brain
Blood clots in the brain can lead to strokes or transient ischemic attacks (TIAs). They disrupt blood flow to brain tissue, which can cause permanent damage if not treated quickly. Symptoms may include:
Sudden, severe headache
Vision problems, such as blurred or double vision
Difficulty speaking or forming sentences
Weakness or numbness on one side of the body
Recognizing these signs early and seeking emergency care can significantly improve outcomes. Clots in the brain require rapid intervention, sometimes including clot-dissolving medications or surgery.
Blood Clots in the Heart
Though less common, clots can also form in the heart, potentially leading to a heart attack. Warning signs include:
Chest pain or pressure
Shortness of breath
Mild headache or dizziness
Clots in the heart can restrict blood flow to vital heart tissue, causing permanent damage. Immediate medical attention is crucial to reduce complications.
Who Is at Risk?
Blood clots are more common in older adults, especially those over 65, and individuals with obesity or a sedentary lifestyle. However, they can occur in anyone, regardless of age. Other risk factors include:
Family history of blood clots
Recent surgery or injury
Long periods of immobility, such as long flights or bed rest
Certain medical conditions, including cancer or clotting disorders
Maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, and regularly consulting your doctor if symptoms appear can significantly reduce the risk of dangerous blood clots.
Prevention and Awareness
Early detection is key. Paying attention to your body’s signals can save your life. If you notice swelling, persistent pain, shortness of breath, or unusual headaches, consult a healthcare professional immediately. Blood clot prevention may include:
Staying physically active, especially during long periods of sitting
Hydrating adequately to maintain proper blood flow
Wearing compression stockings if recommended by a doctor
Taking prescribed anticoagulants for high-risk individuals
Ignoring these warning signs can result in severe complications. Your health and safety depend on being vigilant and proactive.
Blood clots are not just a medical issue; they are a serious threat that can affect multiple organs, including the legs, abdomen, lungs, brain, and heart. Understanding the symptoms and knowing when to seek help can prevent long-term damage or even death.
Remember: Early action saves lives. If you notice any symptoms related to blood clots, do not wait—consult a healthcare provider immediately.