Dangerous Signs of a Blood Clot in the Body That Can Destroy a Person
Recognizing the early signs of a blood clot in the body can be life-saving and help you avoid potentially fatal complications. Blood clots, medically known as thrombosis, most commonly form in the veins of the legs and cause deep vein thrombosis (DVT). The danger of a blood clot lies in its often silent presence—it can remain unnoticed for a long time, only to suddenly become life-threatening if it breaks loose and travels to vital organs like the lungs or heart.
What Is a Blood Clot and Why Is It Dangerous?
Blood clotting is a natural and necessary process that helps prevent excessive bleeding when injuries occur. However, when a clot forms inside a vein without an apparent cause, it can obstruct blood flow and lead to serious health problems. Some clots remain stationary and may not cause harm, but others can dislodge and travel through the bloodstream, resulting in conditions like pulmonary embolism (a blockage in the lungs) or even heart attacks and strokes.
Understanding the symptoms of a dangerous blood clot can make a critical difference in seeking timely medical care.
Key Warning Signs of a Dangerous Blood Clot
1. Unexplained Fatigue
Sudden and persistent fatigue without a clear cause may signal a clot affecting circulation in your body. When the body has to work harder to compensate for impaired blood flow, it can lead to feelings of weakness and exhaustion. If this fatigue lasts for an extended period, it could indicate a clot in areas such as the legs, brain, or chest that is compromising normal function.
2. Swelling in the Limbs
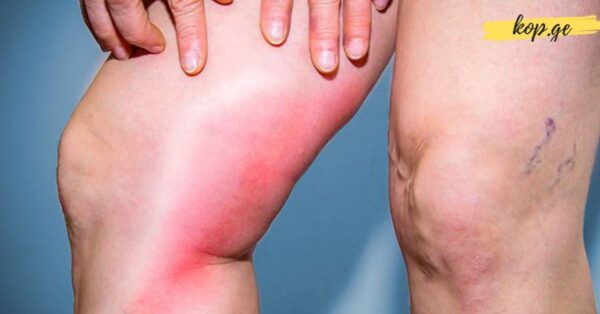
One of the most common signs of a blood clot in the legs or arms is swelling. This occurs because the clot blocks normal blood flow, causing fluid buildup in the affected limb. The swelling may be accompanied by changes in skin color—redness or a bluish hue—and sensations of warmth or itching in the area. This is a serious symptom since a clot in the limb can dislodge and travel to critical organs like the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism.
3. Difficulty Breathing
Shortness of breath or labored breathing can be a sign that a clot has moved to the lungs. When a pulmonary embolism occurs, one of the lung’s arteries is blocked, severely impairing oxygen exchange. This condition requires immediate emergency medical attention. If you experience sudden breathlessness, especially if combined with a persistent cough, you should seek medical help right away.
4. Chest Pain or Pain During Breathing
Chest pain that worsens when you breathe deeply or cough may indicate a pulmonary embolism. The clot obstructs blood flow in the lungs and causes significant discomfort. Similarly, chest pain can also suggest a clot near or in the heart, potentially signaling a heart attack. This symptom should never be ignored.
5. Fever and Excessive Sweating
Though less well-known, fever and increased sweating can occur if a clot forms in the kidneys or other organs. This happens because the clot interferes with the body’s ability to process waste, potentially causing high blood pressure and kidney failure. In such cases, the fever and sweating are signs of an ongoing inflammatory response.
6. Rapid Heartbeat
An unusually fast heartbeat or palpitations can be a warning sign of pulmonary embolism. When a clot blocks blood flow to the lungs, oxygen levels drop, and the heart compensates by beating faster to supply oxygenated blood to the body. If you notice your heart racing for no clear reason, especially alongside other symptoms like shortness of breath or chest pain, seek medical evaluation promptly.
7. Persistent Cough
A cough that won’t go away, especially if accompanied by blood-streaked mucus, may indicate a blood clot in the lungs. The clot causes irritation and swelling of the respiratory tract, triggering coughing. This symptom, combined with a rapid heartbeat and difficulty breathing, should be treated as a medical emergency.
8. Severe Headache
Many people experience chronic headaches, but a sudden onset of an extremely severe headache that doesn’t respond to usual medications may signal a clot in the brain’s blood vessels. This condition is serious and can lead to a stroke if not treated urgently. If your headache is unlike anything you’ve had before and is accompanied by confusion, weakness, or vision problems, go to the emergency room immediately.
9. Pain or Sensitivity in a Limb
It can be difficult to know if you have a clot without medical tests, but pain in a limb without injury is a common sign. If you feel sharp or persistent pain when touching or pressing on your arm or leg, especially if it worsens with movement like walking or bending, it could be deep vein thrombosis. Sometimes the pain may radiate to both legs even if the clot is in only one.
What Causes Blood Clots?
Blood clots can develop due to various reasons:
Immobility: Long periods of inactivity (such as during long flights or bed rest) increase the risk.
Genetics: Some people inherit clotting disorders.
Hormonal changes: Pregnancy, birth control pills, or hormone replacement therapy can increase clotting risk.
Injury or surgery: Tissue damage triggers clot formation.
Chronic diseases: Conditions like cancer, heart disease, or autoimmune disorders raise the risk.
Smoking and obesity: Both contribute to poor circulation and higher clot risk.
What Should You Do If You Suspect a Blood Clot?
If you recognize any of the above symptoms, do not delay seeking medical attention. Blood clots can rapidly become life-threatening. Medical professionals can diagnose clots through imaging tests and blood work and offer treatments like blood thinners to prevent complications.
Prevention Tips
Stay active and avoid sitting still for prolonged periods.
Maintain a healthy weight and balanced diet.
Stay hydrated.
Avoid smoking.
Follow doctor’s advice if you have a history of clotting disorders or are at risk due to medications or medical conditions.
Blood clots may seem invisible and silent, but their impact can be catastrophic if ignored. Recognizing the warning signs and acting promptly could save your life or that of someone you love. Never underestimate unexplained fatigue, swelling, chest pain, or sudden shortness of breath—these symptoms deserve immediate medical evaluation.